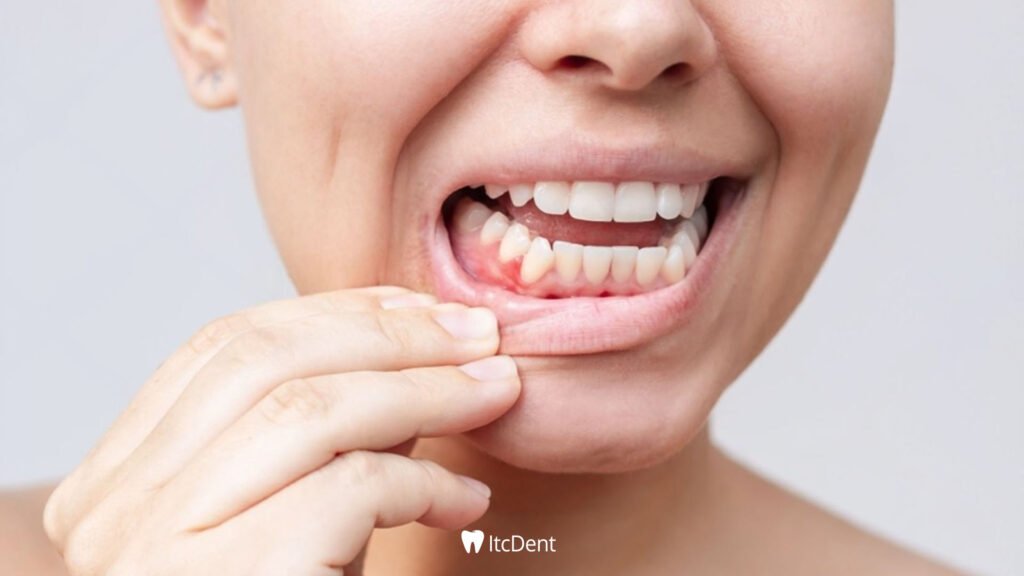
Gum Swelling, although it is a very common problem in oral health, it is often neglected or underestimated. This problem, which manifests itself with a red, sensitive and swollen appearance, can both negatively affect daily life and be a sign of more serious oral and dental health problems.
Gum swelling may start as a simple discomfort; For example, inadequate cleaning of the teeth, accumulation of food residues, or lack of dental floss may trigger this condition. However, when you get to the root of the problem, you may encounter more serious causes ranging from gingivitis to periodontal diseases. In addition, factors such as hormonal changes, vitamin deficiencies, smoking or incorrect dental treatments may also play a role in the development of this disorder.
If gum swelling is not taken care of, you may encounter problems that may affect not only oral health but also your general health. Research shows that oral health has a direct impact on heart disease, diabetes, and even the immune system. Therefore, it is extremely important that even a seemingly simple symptom of gum swelling be taken seriously and its causes evaluated correctly.
What is Gum Swelling?
Gingival swelling is the inflammation and swelling of the soft tissues surrounding the teeth. Swollen gums often turn a dark red rather than pink color and can cause pain when touched. Gum swelling is often accompanied by other symptoms such as bleeding gums, bad breath, and discomfort while eating.
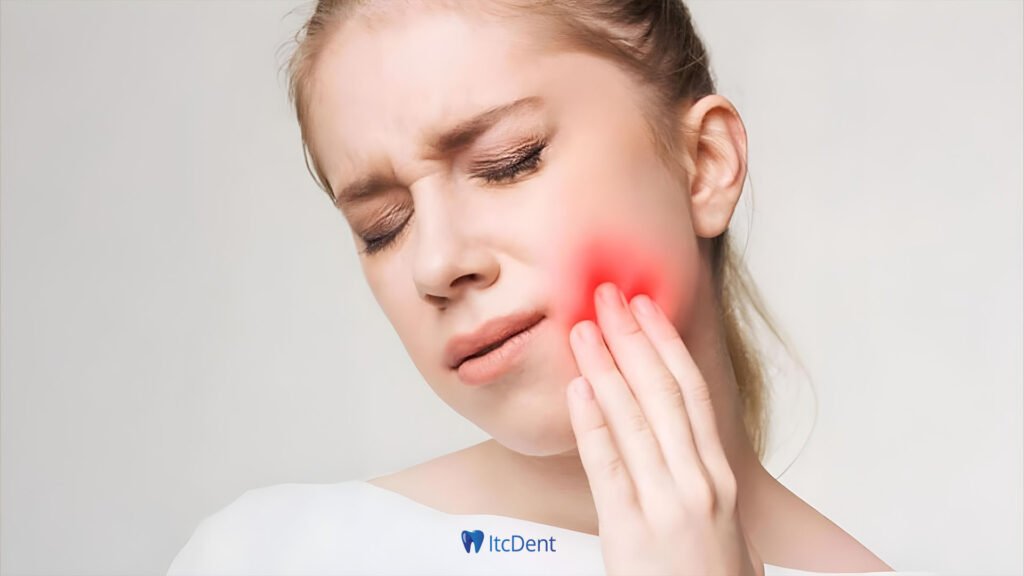
Causes of Gum Swelling
Inadequate Oral Hygiene
One of the most common causes of gum swelling is not paying enough attention to oral hygiene. Not brushing your teeth regularly and not using dental floss causes plaque formation, which leads to bacterial accumulation on tooth surfaces. If left untreated, plaque hardens and turns into tartar, which can cause inflammation in the gum tissues. This inflammation manifests itself with gum swelling. Additionally, lack of oral hygiene threatens not only the gums, but also the integrity of the teeth and general oral health in the long term.
Gum Diseases
Gingivitis (inflammation of the gums) and periodontitis are the main types of gum diseases and are among the most important causes of gum swelling. Gingivitis usually occurs when oral hygiene is not taken into consideration and manifests itself with symptoms such as redness, tenderness and swelling in the gums. If left untreated, this condition can develop into a more serious form called periodontitis. Periodontitis can affect not only the gums but also the bone tissue surrounding the teeth, leading to tooth loss.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations can directly affect gum health, especially in women. Hormonal changes such as pregnancy, puberty, menstruation and menopause can make gums more sensitive, increasing the risk of swelling and bleeding. Increased blood circulation and hormone levels during pregnancy make the gums more susceptible to bacteria, which can lead to a condition called “pregnancy gingivitis.”
Wrong Dental Care Habits
Incorrect dental care methods can cause physical damage to the gums. Especially using a hard-bristled toothbrush or brushing the teeth with excessive pressure causes irritation and swelling of the gums. Since gum tissues are sensitive, such habits can cause wear on both the gums and the tooth surface.
Use of Cigarettes and Tobacco Products
Cigarettes and other tobacco products are one of the main factors that negatively affect gum health. Tobacco products prevent sufficient oxygen and nutrients from reaching the gums, causing the tissues to weaken and increasing the risk of infection. However, the symptoms of gum disease in smokers are often hidden, making it difficult to notice the problem.
Symptoms of Gum Swelling
Symptoms of gum swelling may vary from person to person, but common symptoms include:
- Redness and tenderness in the gums
- Pain while eating or brushing teeth
- Bad breath (halitosis)
- Bleeding gums
- Gums receding or tooth roots exposed
- Feeling of loosening in teeth
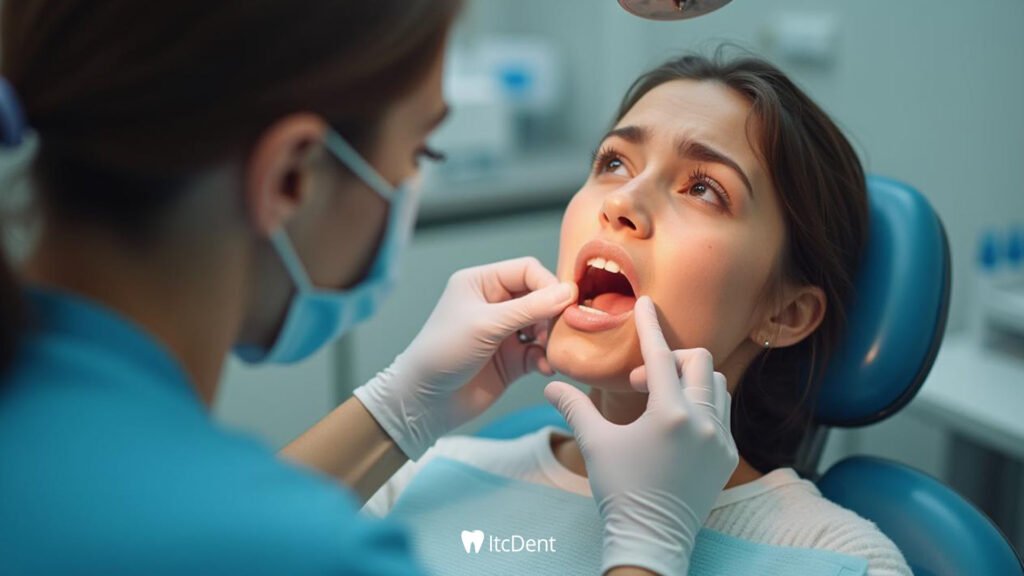
Treatment of Gum Swelling
Treatment of gum swelling varies depending on the underlying cause. Here are common treatment methods:
- Dental Scaling: You can have dental scaling to remove plaque and tartar accumulation. This process will help reduce gingivitis.
- Gum Disease Treatment: Conditions such as gingivitis or periodontitis may require further treatments. Deep cleaning (root planing and curettage), antibiotic treatment, or surgical intervention may be required.
- Vitamin Supplements: If gum swelling is caused by vitamin deficiency, supplements such as vitamin C or vitamin D can be taken.
- Improving Oral Hygiene: Brushing your teeth at least twice a day, flossing, and using mouthwash regularly can improve gum health.
- Avoid Tobacco Products: Quitting cigarettes and other tobacco products positively affects gum health.
How to Prevent Gum Swelling
You can try the following steps to prevent gum swelling.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Do not forget to have your regular dental checkup.
- Correct Brushing Techniques: Use a toothbrush according to your teeth and brush your teeth gently.
- Healthy Diet: Support gum health by following a diet rich in vitamins and minerals.
- Avoid Stress: Stress can weaken the immune system and lead to gum problems. So avoid stress as much as possible

Gum Swelling in Children
Gum swelling in children is a common oral health problem and is often associated with teething periods, poor oral hygiene, or infections. This condition manifests itself with symptoms such as redness, tenderness and swelling of the gums and can cause discomfort in eating, speaking and daily activities in children.
One of the most common causes of gum swelling in children is teething. During this process, gums may naturally become swollen and tender. However, poor oral hygiene is also an important factor. If children do not brush their teeth regularly, it can cause plaque accumulation and thus gingivitis. Additionally, viral infections (for example, herpes virus) or injuries can also cause gum swelling.

