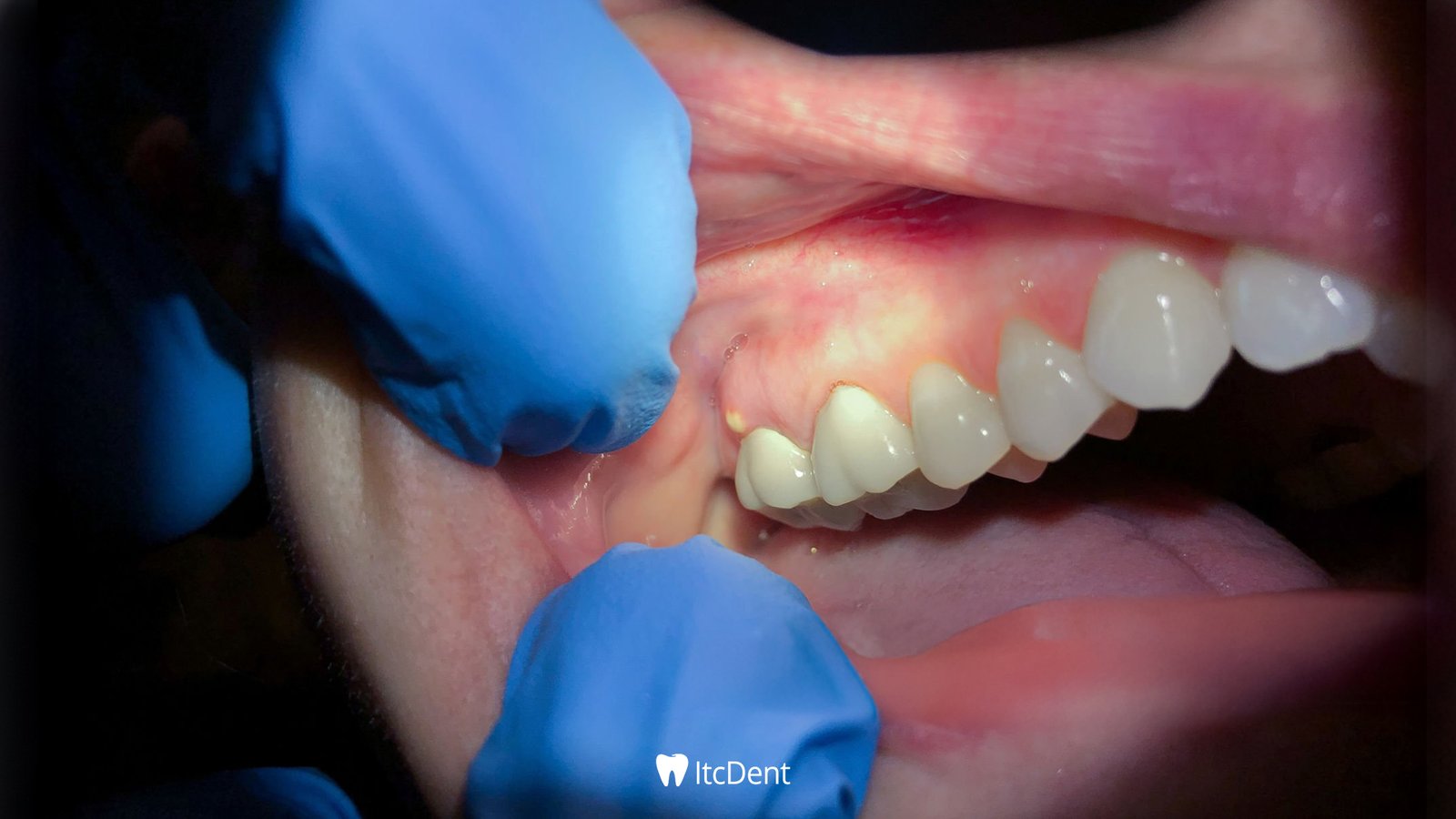
What is Dental Inflammation?
The teeth in our mouths aren’t just hard structures that help us chew food; they’re also an important indicator of our overall health. Healthy teeth are one of the cornerstones of a healthy life. Any dental problem isn’t limited to just the mouth and jaw; it can trigger a host of systemic conditions, from heart disease to digestive issues. Therefore, maintaining oral health is crucial not just for aesthetics or comfort, but for overall overall health.
In this article, we’ll discuss a common yet often overlooked problem: gingivitis. This condition, which can manifest as a mild redness or throbbing pain at the gum line, can lead to serious health problems if left untreated. So, what is gingivitis?
What is Tooth Infection?
Dental inflammation is a type of infection that occurs in the tooth structure or surrounding tissues, usually of bacterial origin. This infection can affect the soft tissue inside the tooth called the “pulp,” the roots, or the gums and bone surrounding the tooth. Tooth inflammation can manifest in various ways; sometimes it manifests as mild tenderness or pain, while in other cases, it can present with more serious symptoms such as severe throbbing, facial swelling, or fever.
The most common cause of tooth inflammation is bacteria accumulating in the mouth, which penetrates the tooth enamel and reaches deeper tissues. Untreated cavities, gum disease, or trauma, in particular, can cause bacteria to reach the root of the tooth and cause infection. When the tooth’s pulp becomes inflamed, the nerves and blood vessels within are affected, which can lead to severe pain. If left untreated, the inflammation can spread to the root apex, causing abscesses in the bone surrounding the tooth and even bone loss.
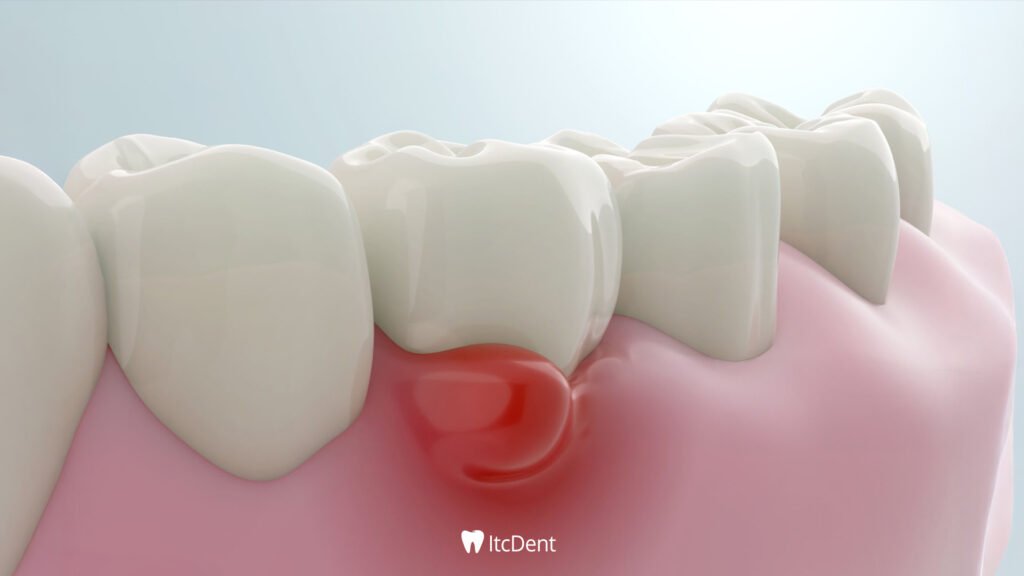
What Causes Tooth Infection?
There are many different factors that can cause tooth inflammation. Sometimes, even minor negligence or habits we make without even realizing it can lead to serious infections over time. Tooth inflammation can occur due to the following reasons:
Tooth Decay
One of the most common causes is tooth decay. Bacteria in the mouth convert the sugary and starchy foods we consume into acid, damaging tooth enamel. While this damage is initially limited to the surface, over time, the decay deepens and reaches the inner part of the tooth, the pulp tissue, where the nerves are located. At this point, bacteria can easily multiply and cause inflammation.
Gum Disease
Healthy gums surround our teeth like a protective shield. However, gum disease—especially gingivitis (gum inflammation) and periodontitis (advanced gum disease)—leads to the breakdown of this protective structure. When the gums recede, bacteria can travel to the root surface of the tooth, causing infection. If timely intervention is not given, this condition can threaten both the tooth and the surrounding bone tissue.
Impacts and Tooth Fractures
Sudden blows to the tooth, or cracks and fractures that occur, can also lead to infection. Even if the tooth appears healthy from the outside, unseen damage to the internal tissues—especially the nerves—may have occurred. This condition usually manifests as pain and can, over time, lead to nerve tissue death and inflammation.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Not brushing regularly, flossing, or maintaining good oral hygiene can easily allow bacteria to accumulate in the mouth. These bacteria first form plaque on the tooth surface, then penetrate the gum line and deeper tissues. As a result, gum disease can occur, followed by inflammation of the tooth root.
What are the Symptoms of Gingivitis?
Gingivitis can progress insidiously. While initially only a mild discomfort, the pain can become unbearable over time. Here are the symptoms to watch out for:
- Constant or throbbing toothache
- Sensitivity to hot and cold
- Increased pain when chewing
- Swelling, redness, or abscess formation in the gums
- Foul odor or taste coming from the gums
- Discoloration of the teeth (graying or darkening)
- Swelling in the face, jaw, or neck
- Fever and fatigue (in advanced cases)
If you experience one or more of these symptoms, you should see a dentist immediately.
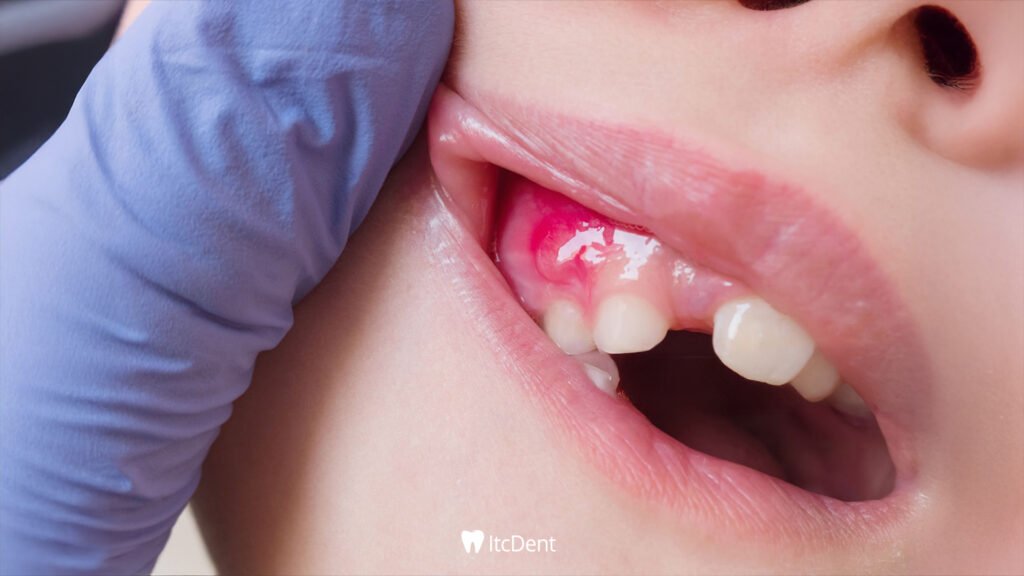
How to Treat Tooth Infection?
Treatment for tooth infection can vary depending on where the infection is located and how far it has progressed. In some cases, a simple procedure may be sufficient, while others may require more extensive treatment. Here are the most common methods:
Antibiotic Use
If the infection has spread or if symptoms such as swelling and fever are present, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics. However, there’s an important point: antibiotics only provide temporary relief. While they may relieve pain and slow the spread of inflammation, they don’t offer a permanent solution unless the root cause of the infection is addressed.
Root Canal Treatment (Endodontics)
If the infection has spread to the pulp tissue, the innermost layer of the tooth, a root canal treatment is usually necessary. During this procedure, the infected nerve tissue is completely removed, the inside of the tooth is disinfected with special solutions, and then filled with a suitable material. Properly performed root canal treatment eliminates the inflammation and allows the tooth to function for many years.
Abscess Removal
In some cases, inflammation can form an abscess (a pus-filled swelling) at the root of the tooth or in the gum area. In this case, the accumulated pus needs to be drained. This procedure is usually performed through a small incision under local anesthesia, and the patient experiences immediate relief.
Tooth Removal
Unfortunately, in some cases, the tooth may be so damaged that it is no longer salvageable. In such cases, extraction may be necessary to prevent the spread of infection and protect the surrounding tissues. This is usually a last resort, but it is sometimes the most effective way to maintain oral health.
Home Remedies
Of course, tooth infection is a serious condition and requires professional treatment. However, some simple measures can alleviate symptoms:
- Gargling with salt water: Gargling with warm salt water several times a day can reduce bacteria.
- Cold compress: If there is swelling in the cheek, a cold compress can be applied externally.
- Pain relievers: A pain reliever such as ibuprofen can be used temporarily. However, this solution is only effective in the short term.
These methods are not a substitute for treatment; they can only provide relief until you can see a dentist.
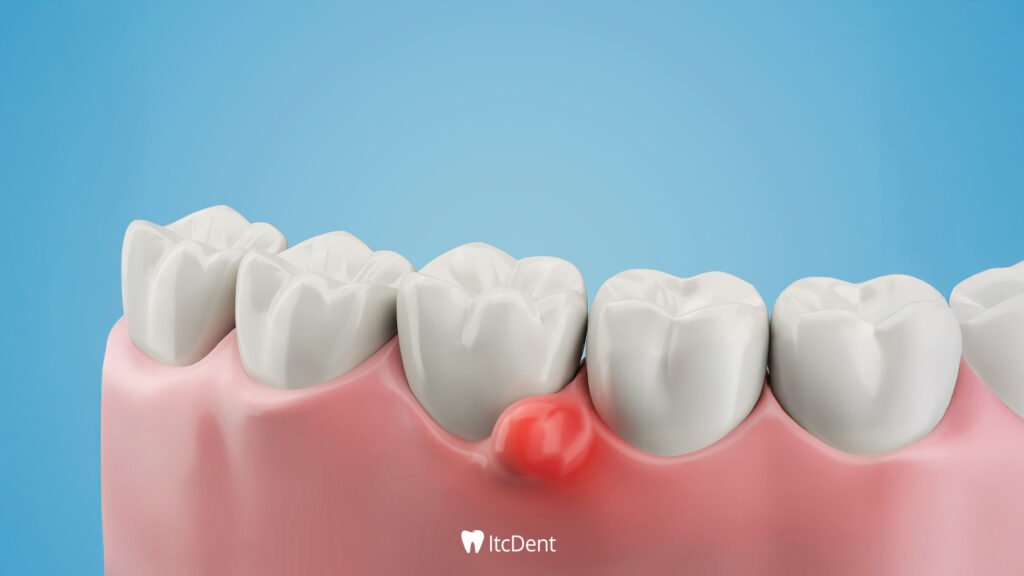
How to Prevent Tooth Infection?
It’s much easier to prevent tooth infection than to treat it. Here are some important points to keep in mind:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day.
- Floss once a day.
- Avoid consuming excessively sugary foods and drinks.
- See your dentist regularly (at least twice a year).
- Don’t forget to have your teeth cleaned.
- Seek immediate attention for any oral trauma or broken teeth.

