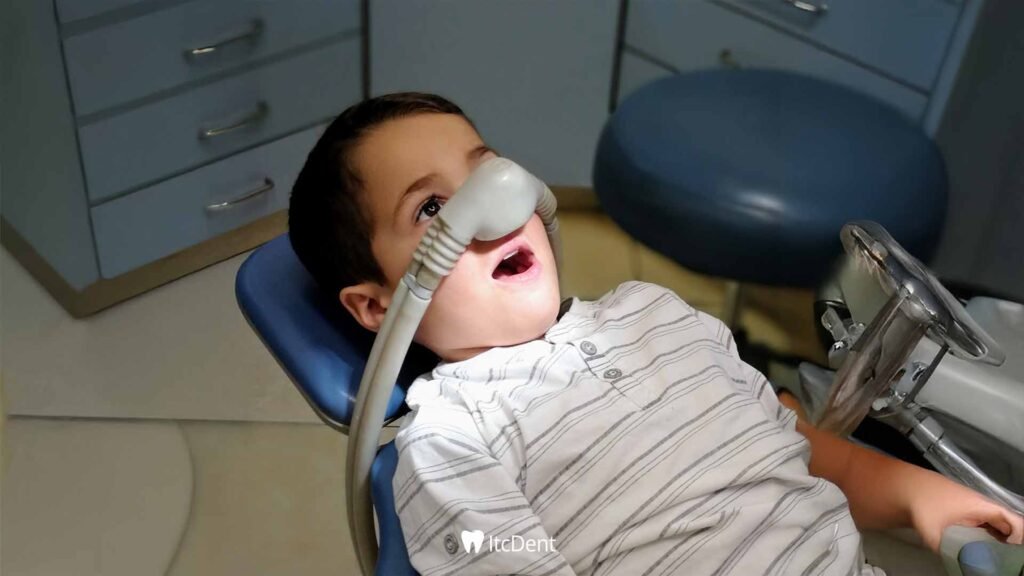
Dental Treatment with Sedation
Fear of the dentist is much more common than people realize. Many people postpone visiting the dentist due to past negative experiences, fear of needles, pain, or fear of losing control. These fears grow over time, leading people to ignore not only routine checkups but even serious dental problems. Unfortunately, this can lead to the need for more complex and painful treatments in the future.
This process becomes particularly challenging for children, individuals with special needs, those with mental or physical disabilities, and adults experiencing dentist phobia. This is where sedation comes into play. Dental treatment with sedation is a safe and effective solution that provides both physical and psychological comfort. During treatments that take longer or involve multiple procedures, the patient is encouraged to relax, feel at ease, and navigate the process without experiencing anxiety. This method makes dental treatment not a source of fear, but rather an easily overcome step.
What is Sedation?
Sedation is a medical procedure used to relax and calm the patient, whether consciously or unconsciously. In dentistry, sedation is used to reduce patient anxiety during treatment, alleviate pain, and facilitate the procedure. This procedure allows the patient to be both physically and psychologically comfortable during the procedure.
Sedation is different from anesthesia. While anesthesia generally refers to a state in which the patient loses complete consciousness, sedation typically results in a light sleep, unaware of surrounding activity, but basic reflexes such as breathing are maintained.
Types of Sedation
The sedation methods used in dentistry are determined by many factors, including the patient’s age, general health, anxiety level, and the duration of the procedure. The goal is to ensure the patient completes the treatment comfortably, painlessly, and without anxiety. Sedation methods used can range from mild relaxation to complete unconsciousness. Here are the most common types of sedation used in dentistry:
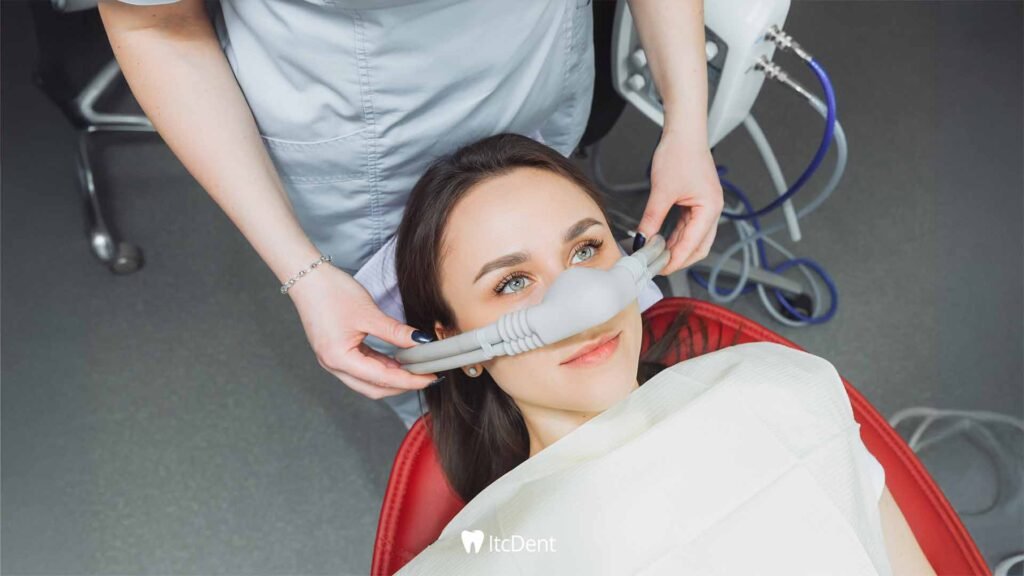
Light Sedation (Minimal Sedation)
In this method, the patient is fully awake but feels more relaxed and calm. It is usually achieved by sedatives taken orally or nitrous oxide, also known as “laughing gas.” It is particularly preferred for patients and children who feel mildly uneasy in the dental chair. Because the patient remains conscious, they can communicate with the dentist and respond to instructions.
Moderate Sedation (Conscious Sedation)
At this level, the patient falls into a semi-asleep state, with reduced awareness of their surroundings. Thanks to intravenous medication, the patient remembers almost nothing during the procedure. However, they can be awakened by mild stimulation and respond to simple commands when necessary. This method is highly effective for individuals experiencing more intense anxiety during dental treatment.
Deep Sedation
Under deep sedation, the patient becomes unconscious and unable to respond to external stimuli. However, some basic reflexes (such as swallowing or blinking) remain. Breathing often requires assistance, and therefore, the patient’s vital functions are carefully monitored during the procedure. It is used in long-lasting, complex procedures or in individuals with high levels of phobia.
General Anesthesia
This is the most intense form of sedation. The patient becomes completely unconscious and may not be able to breathe on their own, requiring ventilator support. It is usually administered in a hospital or operating room setting. In dentistry, it is only used in cases of necessity or when other methods are inadequate. It is particularly suitable for very young children, individuals with mental or physical disabilities, or those undergoing major surgical procedures.
Who Is Sedation Suitable For?
While sedation is not suitable for every patient, it can provide significant relief in certain situations. For individuals who experience excessive anxiety during dental procedures, sedation makes treatment both physically and psychologically more comfortable. Young children may find it difficult to remain still for extended periods or cooperate with the dentist during dental treatment; sedation facilitates a calmer experience.
Similarly, sedation offers significant advantages for the safe and effective treatment of individuals with mental or physical disabilities. It is a preferred method for preventing patient fatigue during long sessions involving multiple procedures and ensuring a smooth and efficient treatment. Furthermore, for patients who exhibit an excessive gag reflex during oral procedures, sedation not only ensures comfort for the patient but also makes the procedure easier for the dentist.
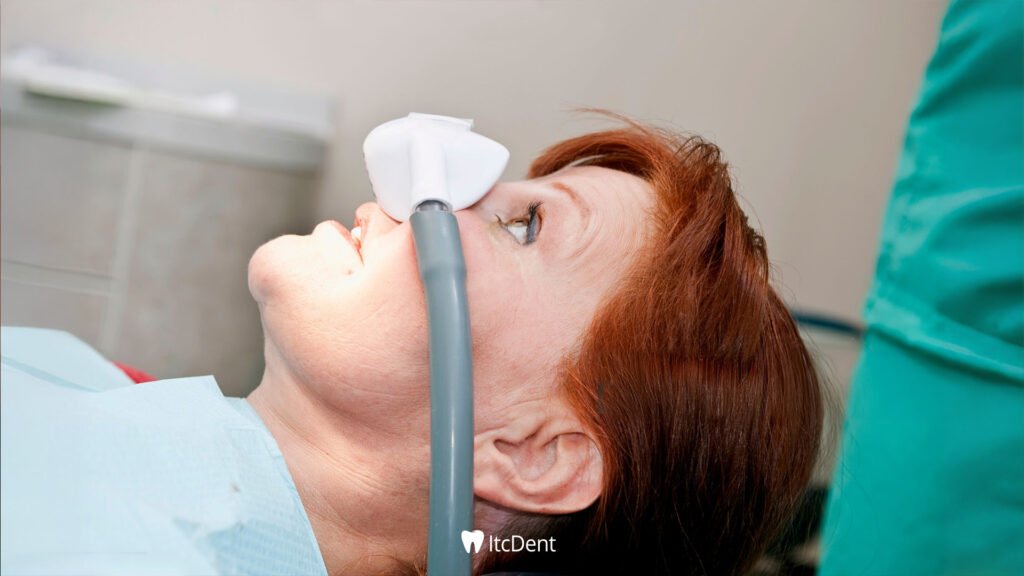
How is Sedation Administered?
While sedation administration varies depending on the chosen method, it is generally a controlled and planned process. Oral medications or laughing gas are generally sufficient for light sedation, while intravenous medications are used for moderate and deep sedation. The first step in the procedure is a preliminary interview and detailed assessment of the patient. During this phase, the patient’s general health, past medical history, allergies, and current medications are carefully examined. A suitable sedation type is then determined for the patient’s needs and duration of treatment.
Before the procedure, the patient is asked to fast for several hours, and vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels are monitored through monitors throughout the procedure. After the prescribed sedation method is applied, the patient gradually begins to relax, and the treatment begins. During this period, an anesthesiologist or a physician experienced in sedation constantly monitors the patient and intervenes as necessary. After the treatment is completed, the patient is kept under observation for a period of time and is discharged after being fully recovered. This ensures a safe and comfortable dental treatment.
Is Sedation Safe?
Sedation is a very safe procedure when administered by an experienced team. However, as with any medical procedure, sedation carries some risks. Therefore, a thorough health assessment should be performed before the procedure.
Possible risks:
- Mild nausea
- Feeling dizzy upon awakening
- Mild pain or bruising when the IV is inserted
- Allergic reactions or breathing problems, although rare, may occur.
These risks are minimal thanks to proper administration and a professional team.
Anesthesia Dental Treatment Prices
Prices for dental treatments performed under anesthesia can vary depending on the type of anesthesia used (local, sedation, general), the duration and extent of the procedure, the patient’s age and health, and the clinic’s location. This method is often preferred for children, individuals with special needs, or patients with dental phobia, but it can incur additional costs. For up-to-date and accurate pricing, please contact the relevant clinic directly.

