What Causes Gum Inflammation?
Oral and dental health isn’t limited to simply having an aesthetically pleasing smile; it’s one of the most important components of our overall health. Healthy teeth allow us to eat, speak, and express ourselves with confidence, while healthy gums are the invisible yet most critical supporter of this process. Gums are the primary structure that protects, stabilizes, and connects teeth to the jawbone. Therefore, no matter how strong and well-cared for teeth, if they are unhealthy, oral health isn’t truly protected.
Gingivitis, a common condition in society, is often overlooked because it initially presents with mild symptoms. However, if it’s not recognized and treated promptly, it can progress to more advanced stages and progress to serious gum diseases like periodontitis. This can cause irreversible damage not only to the gums but also to the teeth, even leading to tooth loss.
Gingivitis isn’t just an oral problem. Research has shown that gum health can be linked to many systemic diseases, from cardiovascular disease to diabetes. This means neglecting oral and dental health can negatively impact not only our teeth but our entire body. Therefore, recognizing gingivitis early, understanding its symptoms, and taking the necessary precautions are crucial.
What is Gingivitis?
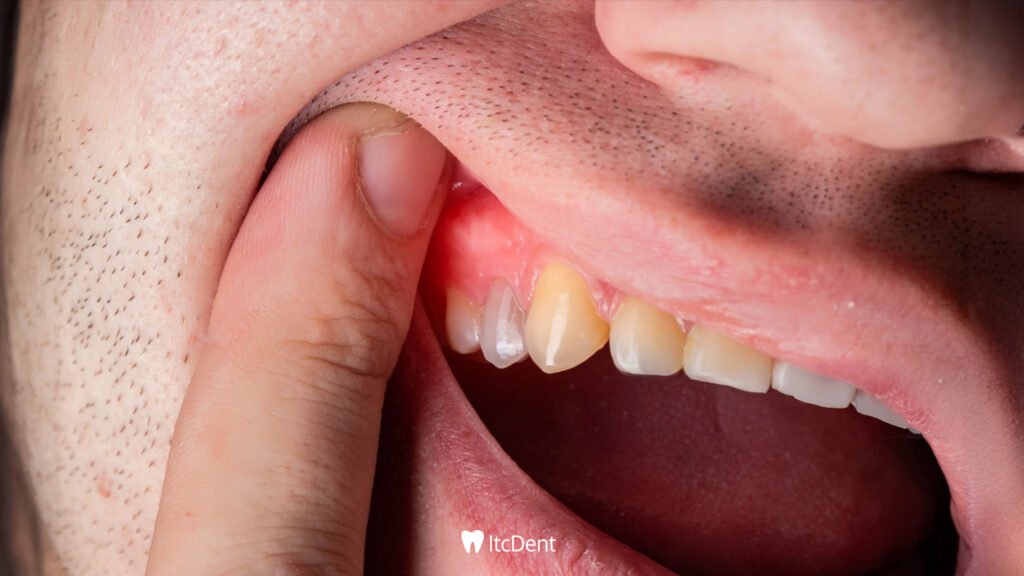
Gingivitis, or gum inflammation, is a common condition caused by bacterial buildup in the gums. It often manifests itself with symptoms such as redness, swelling, tenderness, and bleeding easily when brushing. The primary cause is bacterial plaque, which builds up on tooth surfaces that are not cleaned regularly.
In the early stages of the disease, the problem is limited to the gums, and symptoms are mild. However, if the necessary precautions are not taken during this period, the condition can progress to a more serious form of gum disease called periodontitis. Periodontitis affects not only the gums but also the bone tissue that supports the teeth, causing permanent damage and even tooth loss.
Causes of Gingivitis
Many different factors play a role in the development of gingivitis. Sometimes our daily habits, and sometimes natural changes in our bodies, can contribute to this problem. Let’s take a closer look at the main causes of gingivitis:
Poor Oral Hygiene
The most common cause is not cleaning our teeth regularly and properly. Bacterial plaque accumulates on unbrushed tooth surfaces and hardens over time, turning into tartar. This hardened layer irritates the gums and causes inflammation. This seemingly simple oversight can actually lead to serious gum problems in the long run, even leading to tooth loss.
Smoking
The impact of smoking on the gums is far greater than we think. Smoking disrupts blood circulation to the gums and weakens the immune system, making it harder to fight inflammation. Furthermore, gum disease often progresses more rapidly in smokers, making it more difficult to respond to treatment.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes experienced during periods such as pregnancy, puberty, menstruation, or menopause make the gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation. “Pregnancy gingivitis” is particularly common during pregnancy. It is crucial to maintain good oral hygiene during this period.
Immune System Diseases
Diabetes, HIV, or similar chronic conditions weaken the body’s defenses. When the immune system is weakened, it becomes more difficult to fight bacteria in the mouth, making gingivitis more likely to develop.
Improper and Inadequate Nutrition
When the body is deficient in the vitamins and minerals it needs, the gums are affected. Vitamin C deficiency, in particular, causes gums to weaken and become more prone to inflammation. A balanced diet is crucial for oral health, just as it is for our overall health.
Medication Use
The side effects of some medications can directly affect the gums. For example, antidepressants, blood pressure medications, or immunosuppressants can cause dry mouth. Without sufficient saliva in the mouth, bacteria can grow more easily. Furthermore, some medications can directly cause gum swelling.
Calcium Tartar
Calcium tartar is both a cause and a persistent trigger of gingivitis. Plaque that is not removed promptly hardens into tartar, and these hardened deposits continually irritate the gums, causing the inflammation to become chronic.
Symptoms of Gingivitis
Detecting gingivitis early is crucial to prevent its progression. The most common symptoms include:
- Bleeding from the gums when brushing or eating
- Swollen and red gums
- Bad breath
- Sensitivity and pain in the gums
- Persistent plaque or tartar buildup around the teeth
- Loose teeth in advanced stages
If even one of these symptoms is present, it’s important to see a dentist immediately.
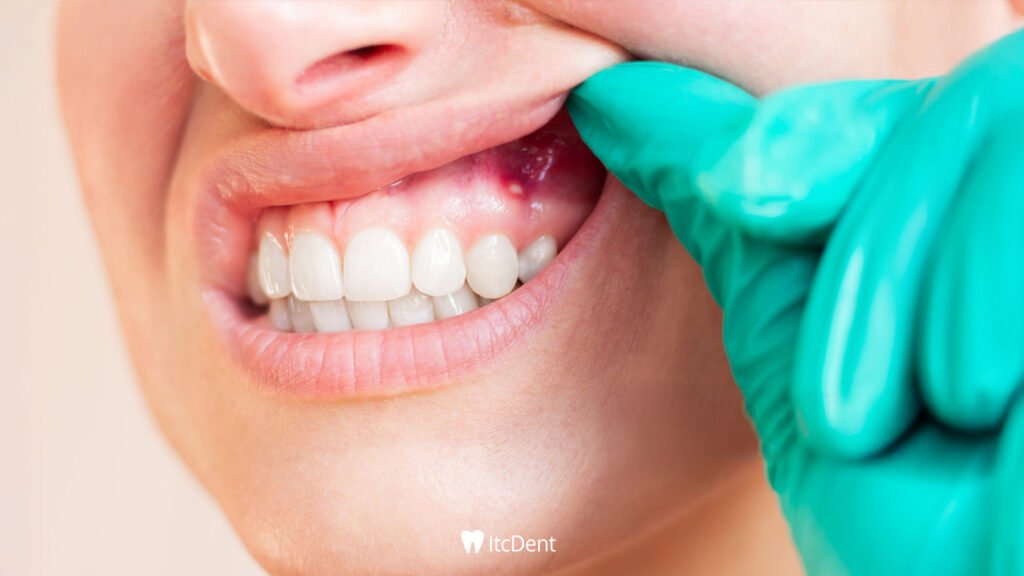
How to Treat Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a treatable condition, but treatment varies depending on the stage of the disease and the individual’s oral care habits. In the early stages, regular and proper oral care—brushing at least twice a day, flossing, and rinsing with an antiseptic mouthwash—is usually sufficient.
However, if plaque has turned into tartar, brushing alone is ineffective, and professional tartar removal by a dentist is necessary. In some cases, antibacterial mouthwashes or antibiotics may be prescribed by the dentist. For successful treatment, quitting smoking, adopting a balanced and vitamin-rich diet, drinking plenty of water, and avoiding stress are also crucial.

