Can an abscessed tooth be extracted?
Dental health is an important part of our general health, and problems in this regard can often cause both physical and psychological discomfort. Tooth abscess is a serious health problem that occurs as a result of inflammation in the teeth. Tooth abscess develops due to infections in the tooth root or gums and is usually manifested by severe pain, swelling and discomfort. These inflammations occur as a result of the spread of bacteria to the inside of the teeth or surrounding tissues, and if left untreated, can lead to serious health problems.
Abscesses often occur as a result of tooth decay, gum disease or dental trauma. If not detected and treated early, dental abscesses can both increase pain and cause the infection to spread to surrounding tissues. This condition can significantly affect a person’s overall health and quality of life.
What is an Abscessed Tooth?
An abscessed tooth occurs when inflammation occurs in or around the roots of the tooth. The formation of an abscess is usually caused by a tooth decay, tooth breakage, or infection of the gum. This inflammation, which accumulates at the root of the tooth, usually causes symptoms such as intense pain, gum swelling and fever. Depending on the area where the abscess is located, the tissues around the tooth may also be affected. So, can a tooth with an abscess be extracted? Let’s examine this together;
Removing an abscessed tooth may be part of the treatment process, but this decision must usually be made by a dentist. Here are some factors that affect the extraction of abscessed teeth:
- Severity and Spread of the Abscess: If the abscess is widespread and the inflammation has progressed to the roots of the tooth, the tooth may need to be extracted. In this case, preserving the tooth may be difficult and extraction may be the most appropriate solution.
- Response to Treatment: Some abscesses can be healed with conservative methods such as antibiotic treatment and root canal treatment. If these treatments are successful, it may not be necessary to extract the tooth. However, if there is no response to treatment, tooth extraction may be considered.
- General Condition of the Tooth: The general condition of the abscessed tooth is also an important factor. If the tooth is decayed or structurally damaged, extraction may be more appropriate. The salvageability and longevity of the tooth should be evaluated.
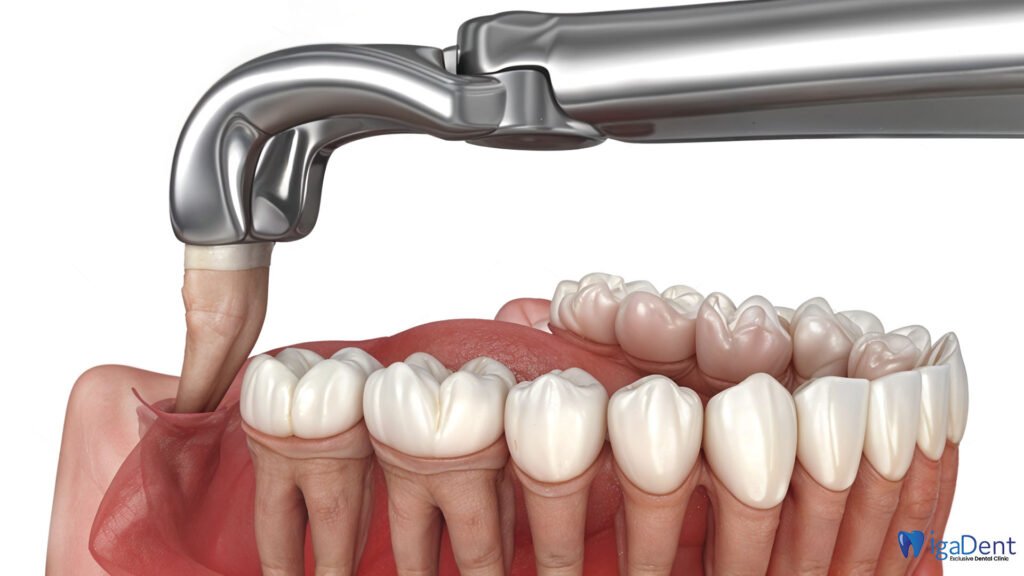
How to Treat Abscessed Tooth?
Treatment methods for abscessed teeth may vary depending on the severity of inflammation and the general condition of the tooth. The first step in the treatment process is usually antibiotic therapy. Antibiotics help control the infection caused by a tooth abscess and can reduce pain and inflammation. In addition to antibiotic treatment, painkillers may also be prescribed. However, it is important to use these drugs in accordance with the dosage and duration recommended by the doctor.
Another important method in the treatment of tooth abscess is root canal treatment. If there is inflammation in the roots of the tooth, this process involves cleaning the inflamed tissue accumulated in the roots of the tooth and sterilizing the inside of the tooth. In root canal treatment, the root canals of the tooth are opened, cleaned and then closed with a special filling material. This method protects the tooth and allows it to continue its function, and after treatment, a coating or filling may often be required on the tooth.
If the roots of the tooth are too damaged or the inflammation is too advanced to be treated, the tooth may need to be extracted. After extraction, various restoration methods can be used to replace the tooth. Dental implants are artificial tooth roots placed in place of the tooth root and offer an aesthetic solution. Additionally, other restoration methods such as dental bridges may also be preferred. These methods help eliminate missing teeth and restore chewing function.
What Happens If an Abscessed Tooth is Extracted?
When an abscessed tooth is extracted, various consequences and healing processes may occur. Tooth extraction is usually preferred if the tooth is too damaged to be healed or the inflammation is too advanced. The extraction process prevents the spread of infection and reduces pain. However, there are some important steps and considerations after tooth extraction.
First, there may be swelling, pain and discomfort in the area after the extraction. Painkillers and anti-inflammatory medications are often prescribed by the dentist to manage these symptoms. It is also important to pay attention to the dentist’s recommendations to promote healing of the area. After extraction, a clot usually forms and this clot plays an important role in the healing process. Keeping the clot in place helps the bone and gums heal. During this process, oral hygiene should be taken care of and the dentist should act as recommended to prevent the clot from disappearing.
After tooth extraction, various restoration methods can be used to replace the missing tooth. These methods include dental implants, bridges or dentures. Implants are artificial roots placed in place of the tooth root and can restore chewing function. Bridges and prostheses fill the missing tooth in aesthetic and functional terms.
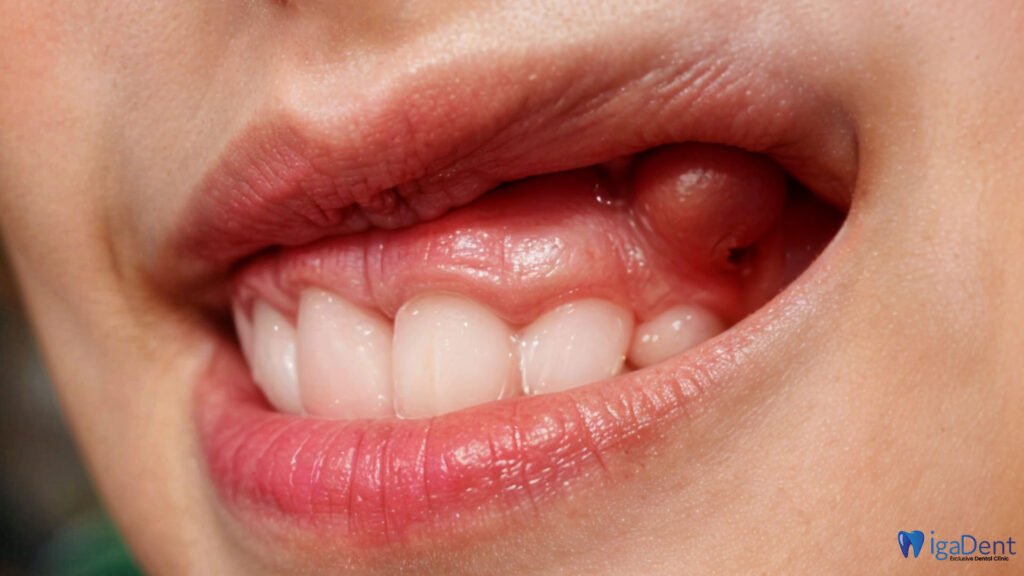
Risks and Aftermath of Extracting an Abscessed Tooth
Removing an abscessed tooth can often be a necessary intervention, but there are some risks and points to consider after this procedure:
- Risk of Infection: The area may become infected after the extraction. Paying attention to oral hygiene as recommended by your dentist and using the prescribed medications regularly can reduce this risk.
- Bleeding and Swelling: Bleeding and swelling may occur after the extraction. This condition is usually temporary and can be managed with cold compress application and doctor’s advice.
- Tooth Loss: Restorative procedures will be required to replace the extracted tooth. Tooth loss can affect chewing function and cause aesthetic problems. Options such as implants or bridges can minimize the effects of tooth loss.


