What is frenectomy?
Oral and dental health is an integral part of our overall health. A healthy oral structure is achieved not only by the good condition of our teeth and gums, but also by the harmony of the tongue, lips and cheeks. One of the main elements that ensure this harmony is the connective tissues inside the mouth, that is, the frenulum.
However, situations that negatively affect the functionality or aesthetic appearance of these tissues may endanger oral health over time. At this point, frenectomy, one of the modern dentistry practices, comes into play.
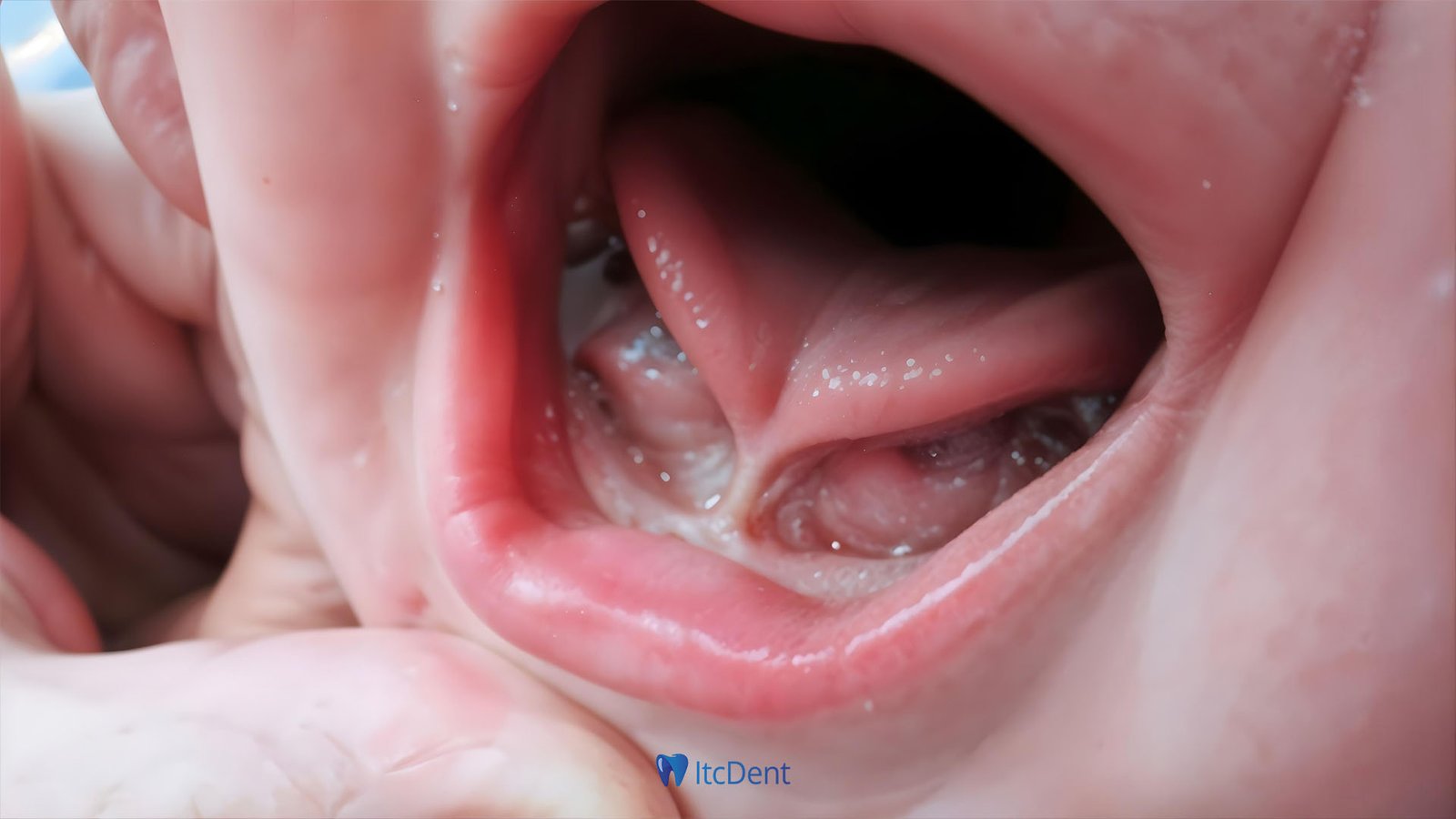
Frenectomy is a procedure that involves surgical correction of the connective tissues inside the mouth called the frenulum. These connective tissues are located in areas such as the sublingual (lingual), upper lip (labial) or cheek and can affect the mobility of these areas. Structural disorders or functional problems of the frenulum can cause serious difficulties in daily life.
For example, a short frenulum under the tongue (ankyloglossia) is colloquially known as “tongue tie” and can especially lead to speech disorders. Problematic frenulum in the upper lip can cause aesthetic concerns by causing gaps (diastema) between the teeth.
Three types of frenulum are most commonly found in the human mouth:
- Lingual Frenulum: It is the thin tissue that connects the lower part of the tongue to the floor of the mouth.
- Upper Lip Frenulum (Labial Frenulum): Connects the upper lip to the upper jaw gum.
- Lower Lip Frenulum: Connects the lower lip to the lower jaw gum.
These connective tissues generally do not cause a functional problem; However, in some cases, especially when it is too short, thick or tight, various problems may occur. In such cases, the frenectomy procedure comes into play.
Why is frenectomy performed?
Frenectomy is a procedure performed to solve various functional and aesthetic problems caused by the connective tissues (frenulum) inside the mouth. Conditions where the tongue frenulum is extremely short or tight, known as tongue tie (ankyloglossia), can lead to difficulty speaking, chewing problems and sucking problems in babies.
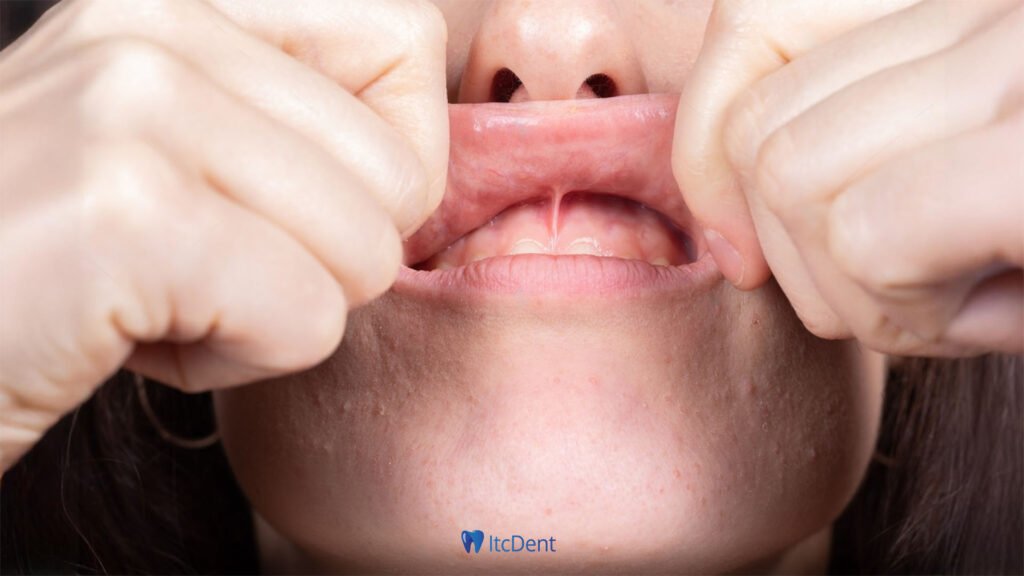
If the upper lip frenulum is too thick or long, it may cause aesthetic concerns by creating a gap (diastema) between the front teeth. Additionally, incorrect positioning of the frenulum in individuals using prosthesis may prevent the prosthesis from fitting properly. Excessive tension of the frenulum on the gums can lead to gum recession and serious gum problems. In addition, structural anomalies may cause speech disorders and limitation of jaw movements.
Who Can Perform Frenectomy?
Frenectomy is an effective surgical procedure that can be applied to all age groups to solve problems caused by the connective tissues in the mouth. This intervention is performed with different techniques depending on the age of the individual, the problem he/she is experiencing and the location of the frenulum. Frenectomy, generally considered a minor and simple surgical procedure, is preferred in the following cases:
- Newborns and Babies
Conditions such as tongue tie (ankyloglossia) can negatively affect the sucking reflex of newborns and lead to feeding difficulties. Restricted tongue movements can also make breastfeeding difficult for the mother. In such cases, early frenectomy allows babies to feed more healthily and improves the mother’s breastfeeding experience.
- Children
Conditions such as tongue tie or length of the upper lip frenulum can cause speech disorders, gaps between teeth and aesthetic concerns in children. In particular, tongue tie can cause speech problems such as the inability to pronounce some letters correctly. Frenectomy performed during childhood can be very effective in solving these problems when applied together with speech therapy. It can also be combined with braces or other orthodontic treatments to close gaps between teeth.
- Adults
Frenulum problems can cause problems not only in childhood but also in adulthood. In individuals using dentures, a large or improperly positioned frenulum may prevent the denture from fitting properly and reduce comfort. Additionally, in cases requiring aesthetic interventions, frenectomy may pave the way for a more beautiful smile design. Frenectomy performed in adults can positively affect speech, chewing and general oral health.
In every age group, the frenectomy procedure, planned in accordance with the patient’s needs and anatomical structure, should be performed by a specialist dentist or surgeon. This intervention aims to improve the individual’s quality of life, as well as to protect oral and dental health in the long term.
How to Perform a Frenectomy
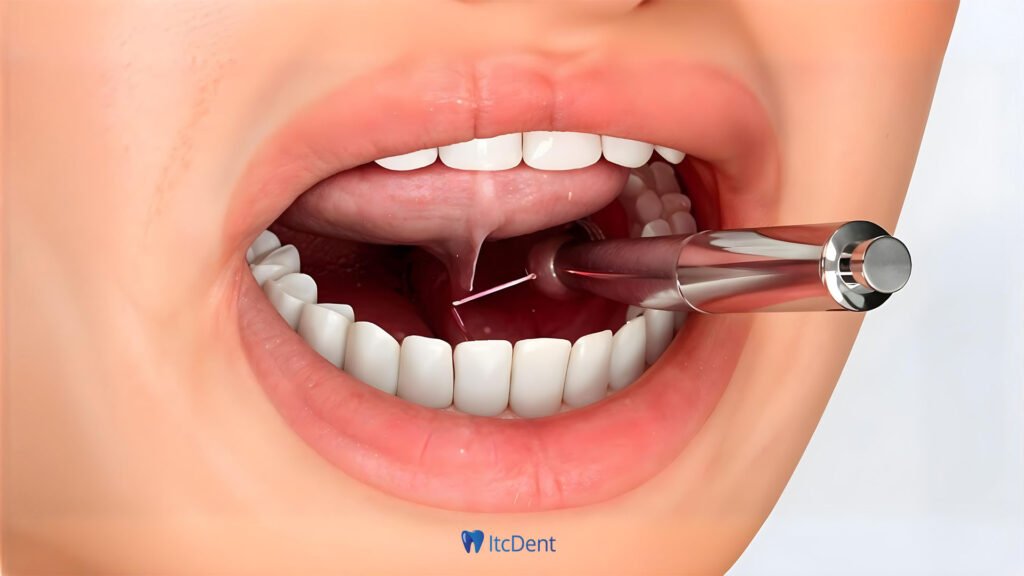
Frenectomy is a simple surgical intervention usually performed by a dentist or oral surgeon under local anesthesia to ensure the comfort of the patient. Before the procedure, the physician examines the patient in detail and evaluates the structure of the frenulum, the problems it causes and the need for intervention. At this stage, procedure planning is made taking into account the patient’s general health condition and needs. By numbing the area with local anesthesia, the patient is prevented from feeling pain or discomfort during the procedure.
During surgery, frenulum tissue is cut using a traditional surgical scalpel or laser technology. Laser technology allows the procedure to be completed faster and safer by minimizing bleeding and reducing the risk of infection. After the procedure, stitches may be placed in some cases to accelerate the healing of the cut area and obtain a smoother result, but this is usually not necessary in laser interventions. Frenectomy is a procedure that is completed in a short time and the recovery process is generally trouble-free, and aims to significantly improve the patient’s quality of life.
Healing Process
The recovery process after frenectomy is usually rapid. After the procedure, patients should pay attention to the following points:
- Hot or spicy foods should be avoided immediately after the procedure.
- Attention should be paid to oral care as recommended by your doctor.
- If pain or swelling is felt, painkillers prescribed by the doctor can be used.
- It may be recommended to do exercises that increase tongue movements or strengthen lip muscles.
For children and infants, assistance may be needed to regulate sucking or chewing during the healing process.

